Are you worried that red light therapy might tan your skin like sunbathing does? It's a common question for anyone new to this gentle skin treatment. This article will explain in simple terms why you won't get a suntan from red light therapy. Unlike the ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun that change your skin color, red light has different wavelengths—between 620 to 750 nanometers—that don't cause tanning. We'll clear up any confusion and discuss why red light can care for your skin without adding any extra color.
What Is the Visible Light Spectrum and Where Does Red Light Fit In?
The visible light spectrum is the range of light that human eyes can see. It includes all the colors from violet to red, each with different wavelengths:
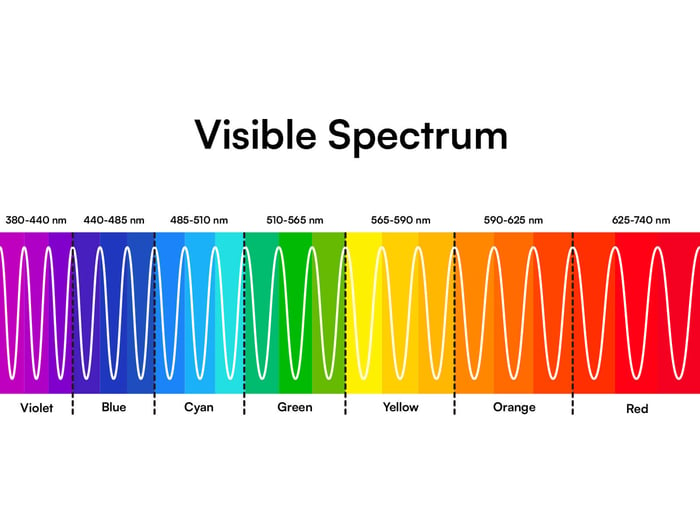
| Color | Wavelength (nm) |
| Violet | 380–450 |
| Blue | 450–485 |
| Cyan | 485–500 |
| Green | 500–565 |
| Yellow | 565–590 |
| Orange | 590–625 |
| Red | 620–750 |
Red light is on the far end of this spectrum, just before infrared light which we can't see. With its longer wavelength, red light is low in energy but it's useful for things like skin treatments because it can go deep into the skin without harming it. However, it's important to understand the potential effects of excessive use, so you might want to read about whether red light therapy can damage skin.
What's the Difference Between Red and Ultraviolet Light?
| Aspect | Red Light | Ultraviolet Light (UV) |
| Wavelength | 620–750 nm |
|
| Visibility | Visible to humans | Invisible to the naked eye |
| Energy Level | Lower energy | Higher energy |
| Skin Penetration | Can penetrate deeply but gently | Varies; can damage DNA and skin cells |
| Health Applications | Promotes healing, reduces inflammation | Sterilization, formation of vitamin D, can cause sunburn and skin aging |
Red Light
Red light has some of the longest wavelengths that we can see, ranging from 620 to 750 nanometers. This is the kind of light you see during a sunset which looks warm. It's not strong enough to hurt our skin like UV light can. Instead, red light is often used to help heal the skin. It goes deep into the skin without causing damage and can help with a bunch of skin problems, make healing faster, lessen swelling, and soothe pain.
How Is Red Light Used?
1. Red light therapy devices are popular for keeping skin healthy and may help reduce wrinkles.
2. Some doctors use red light to speed up the healing of wounds.
3. Red light can ease pain, which is why some therapies for sore muscles use it.
4. Red light helps plants grow, so indoor gardens often use red lights.
Ultraviolet Light (UV)
Ultraviolet light, or UV for short, is made of wavelengths that are too short for us to see. There are three types—UVA, UVB, and UVC. Each type has different levels of energy and can affect our health in different ways. UV light is what gives you a tan or a sunburn if you're out in the sun too much, and it can also make your skin age faster and could lead to skin cancer after a long time. The Earth's atmosphere stops most of the UVC rays, which are the strongest, from getting to us. But UV light isn't all bad—it helps kill germs and is important for making vitamin D in our bodies.
What Are the Uses of Ultraviolet Light?
1. UV light can clean water, air, and surfaces by killing bacteria and viruses.
2. Doctors use UV light for treating skin conditions like psoriasis.
3. A little bit of UV light from the sun helps our body create vitamin D.
4. Some glues and resins need UV light to get hard and stick things together.
5. Forensic teams can use UV light to see things at crime scenes that are invisible to our eyes.
How Does Ultraviolet Light Lead to Tanning and Skin Damage?
Here's a quick look at what ultraviolet light does to the skin:
- UVA rays reach deeper layers of the skin, causing aging; UVB is mainly absorbed by the superficial layer and causes sunburn.
- Both UVA and UVB stimulate melanin, which makes the skin darker.
- UVA is responsible for some effects of aging, such as wrinkling; UVB primarily causes sunburn.
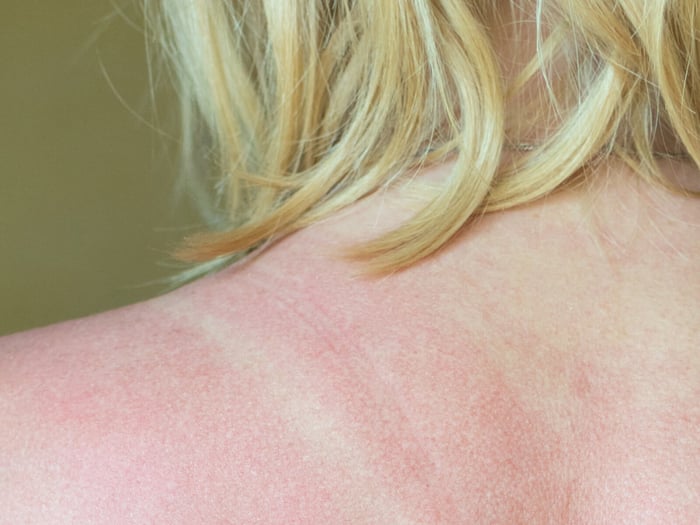
1. UVA rays affect the deeper layers of skin, while UVB rays damage the surface.
In human skin, UVA rays reach deep and are easily apt to cause aging signs such as wrinkles and loss of elasticity. Unlike UVA rays, UVB rays attack the outer layer of skin, thus visible damages like sunburn. UVA acts stealthily to degrade the structure of your skin from within, making it less resilient over a period. UVB rays are essentially responsible for sunburns; these rays attack the topmost skin cells, thus often causing irritation and erythema of the skin. 2. Ultraviolet light stimulates melanin production, thereby darkening the skin.
2. Melanin production increases under ultraviolet light, darkening the skin.
When exposed to UV light, the skin ramps up its melanin production. UVA rays quickly darken existing melanin for a short-lived tan, whereas UVB rays stimulate the body to produce new melanin, c. The fast, temporary tan from UVA rays is just a superficial darkening of existing melanin. In contrast, when UVB rays strike, they initiate signals that let the skin know it needs to ramp up its melanin production. This not only gives you a more pronounced tan but forms a natural barrier to further UV damage.
3. Proper sun protection shields the skin from harmful UVA and UVB rays.
Using broad-spectrum sunscreen defends your skin from the long-term aging effects of UVA rays and the burning caused by UVB rays. To effectively reduce the risk of UV damage, applying a high-SPF sunscreen should be part of your regular skincare routine. Wearing protective, covering clothes, along with staying in the shade whenever the sun is high, are highly preventive steps.
Does Red Light Affect Skin Pigmentation?
No, red light does not stimulate melanin production and therefore has no effect on skin pigmentation or tanning.
Red Light Does Not Stimulate Melanin Production
Melanin is the organic pigment that gives color to our skin, our eyes, and our hair. Its production ramps up when we're exposed to UV light. But what about red light? The longer wavelengths of red light, roughly from 620 to 750 nanometers, lack the energy to excite melanocytes into producing more melanin. This means red light does not cause tanning; it simply lacks the punch on those smooth, red waves to turn on the machinery that makes melanin in our skin cells.
Red Light Therapy Does Not Increase Skin Pigmentation
Most research into red light therapy has focused on its potential benefits to skin health, such as reducing inflammation and accelerating healing. In fact, many studies have shown time and again that among the many responses red light may provoke in the skin, one response it does not is increasing pigmentation. It penetrates the skin to a depth at which the energy can become therapeutic without creating cascading chemical reactions that signal tanning.
Reasons Why Red Light Cannot Cause Tanning
There are some fundamental reasons why sitting under the beam of red light will not provide one with a tanned look at all. These include:
- Red light simply doesn't have the high-energy photons that are needed to induce melanin production like UV rays do.
- Even though red light can penetrate the skin, it does not reach or affect the deeper layers where melanin production occurs.
- Our bodies don't interpret red light as a signal to defend against potential damage by producing more melanin, unlike with the harmful UV radiation from sunlight.
Even though it lights up your skin, red light doesn't have the right kind of wavelengths to create extra color. So if you're using red light therapy for its potential skin-healing benefits, rest assured that an unexpected tan won’t be part of the package.
Red Light Therapy: Get the Skin Benefits Without the Tan
Red light therapy is a skin-friendly option that won't tan you like the sun's UV rays do. Unlike the sun's UVA and UVB rays that make your skin darker and can hurt it over time, red light is gentle. It doesn't tell your skin cells to make more melanin, which is what causes tanning. Studies back this up, showing you can get the good effects of red light—like helping your skin feel better—without changing its color. Give red light therapy a shot for healthier skin – it's a simple and tan-free way to look after your skin.